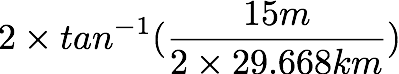WOW – what a clickbait title that is…
Back from having spent a few days between Christmas and New Year in Palma, Majorca. On the last day there I noticed I could just see the dome of the Planetarium of Majorca (or the telescope dome, I’m not sure which) from the hotel terrace. Seeing conditions were not great, but the small white point on the mountain top was clearly visible by reflected sunlight. It did look to be just on the edge of visibility, so now I’m back I wondered just how close to being invisible it really was.
Some Data:
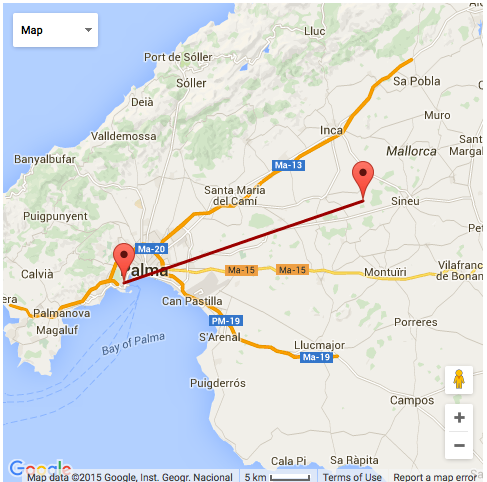
- Telescope dome position : 39.642528°N 2.950516°E (from wikipedia)
- My viewing position : 39.555666°N 2.623219°E (from photographic GPS and google maps)
Some derived data:
- Dome diameter : 15m (measured off google earth)
- Distance between these points : 29.668km
Angular size :
- 5.056×10^-4 radians
- 0.02897 degrees
- 1′ 44.3″ arc seconds
This seems pretty small, how’s it compare to things we’d usually see?
- Sun diameter : 31’30″Full Moon diameter : 29’20”
- Planet Venus at closest : 1’00”
- Brightest star in the sky – Sirius : 0.005936″
(All values from wikipedia)
The dome appears larger than the brightest star in the sky and roughly the same size the planet Venus does. These are both perfectly visible, so why did the dome appear just visible to me? I’m guessing it’s because the dome was only reflecting a small amount of light, and I was viewing it against quite a bright background (blue sky) too. Atmospheric haze and thermal twinkles probably didn’t help.
So although I should have been able to see it pretty clearly (if it had been emitting it’s own light, against a dark background) , I was probably pretty lucky to have seen it at all given the atmospheric conditions.
Happy new year!